What is a rubber conveyor belt?
- The conveyor belt is a key component of a belt conveyor used to transport loose materials or bulky items. It consists of an elastic body (cover rubber and core rubber) and a skeleton material. The basic shape of the conveyor belt is flat, a standardized and international product.
- The conveyor belt has a history of nearly a hundred years. It was first standardized in Britain in 1933. After the 1940s, due to the rapid development of synthetic fibers, synthetic rubbers, and resins, they were directly used in the conveyor belt industry, as well as the progress in the research of steel cord conveyor belts. Make the conveyor belt products change. It fully demonstrates the functionality and economic vitality of the conveyor belt.
- After more than half a century of hard work, modern conveyor belts have solved many problems that were difficult to solve in the past, and are considered to be the most economical and effective way to solve the environment, energy, transportation, space congestion, labor, and production safety in modern material handling and processing. one.
- At present, the main trend of the development of conveyor belts is diversification, high strength, large-scale and light-weight, and strive to improve the conveying capacity, expand the scope of use, overcome the flying and spilling of materials in operation, and the restrictions on the curved operation and conveying slope, and further improve Service life and economic benefit.
- Conveyor belts are widely used in various sectors of the national economy. Supermarkets, factories, mines, farms, warehouses, construction sites, ports, docks, airports, and stations have conveyor belts in use, which are closely related to energy and transportation. The variety, quality, and application of conveyor belts indicate the level of industrialization in a country. At present, the conveyor belt has a broad domestic and international market, but it also faces tremendous pressure to improve performance and reduce costs.
Types of rubber conveyor belts
- Conveyor belts are diverse and new products are constantly emerging, and it is difficult to systematically classify them.
- At present, the common classification methods are: according to the carcass material, there are fabric belts, steel cord belts, and aramid belts;
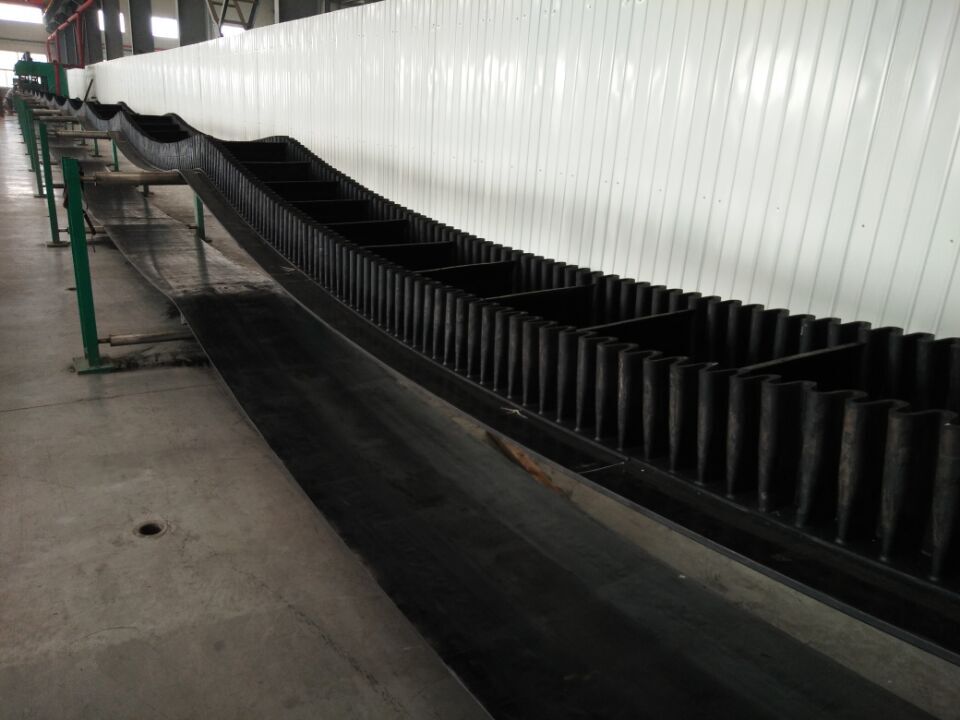
- according to appearance, there are flat belts, light pattern belts, deep pattern belts, sidewall belts, rail guide belts, tubular belts, etc.
- According to the characteristics, there are ordinary belt, cold-resistant belt, heat-resistant belt, oil-resistant belt, Acid and alkali resistant belts, static conductive belts, flame-retardant belts and food belts, etc.;
- according to the number of fabric layers, there are single-layer belts, double-layer belts, multi-layer belts, and PVC/PVG belts;
The carcass material
- The carcass material of the conveyor belt provides the main tensile properties for the conveyor belt and plays an important role in transmitting power, conveying materials, resisting impact, maintaining the correct shape, and running track of the conveyor belt, Therefore, its performance is a key factor in determining the performance, working life and processing methods of the conveyor belt. The main carcass materials for conveyor belts are various fiber fabrics and steel wire ropes.
- The traditional fiber material for the conveyor belt carcass is cotton. The strength of the cotton fiber is low, far inferior to the nylon and polyester that are often used at present. The chemically impregnated nylon and polyester also have good compatibility with rubber. Although the strength of nylon is high, its modulus is low, the elongation is large, and it is easy to deform; the strength of polyester is similar to that of nylon. And its elastic modulus is high and dimensional stability is also good. Therefore, light and flat conveyor belts mostly use polyester as the carcass material, while conveyor belts that require grooves are mostly interwoven with polyester and nylon to maintain warp dimension stability. weft direction is easy to form groove and full of flexibility. All nylon fabrics are suitable for occasions that require greater impact resistance. The steel cord has high strength, small elongation, and good dynamic performance, which is especially suitable for the needs of high-strength and heavy-duty conveyor belts. The application of glass fiber is limited to certain heat-resistant conveyor belts. Aramid has relatively large strength/quality, small elongation, heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and flame retardant, and it is a strong competitor of steel cord conveyor belts.
Rubber and formula
- The wide application of conveyor belts makes its requirements for performance and cost more diversified. There are many types of polymers used in conveyor belts, which can be divided into rubber and resin. The fabric core belt and the steel cord core belt with strength above the middleweight level mostly use rubber, and most of the rubbers used are NR, SBR, IR, and BR. NR has high cutting resistance, SBR is resistant to abrasion, and others such as CR, NBR, EPR, and CIIR are used for conveyor belts with special performance requirements. Silicone rubber and fluorine rubber are also used, but only for the surface layer of certain special performance belts. PVC resin is often used for integral braided core conveyor belts and light conveyor belts. PU resin is mostly used in the food industry.
- The main function of the cover rubber is to protect the belt carcass, to withstand the effects of abrasion, impact, cutting, corrosion, and the atmospheric environment caused by the conveyed materials, and to meet different requirements such as heat resistance, cold resistance, oil resistance, acid and alkali resistance, flame retardancy and static electricity. From a process point of view, the covering rubber compound needs to have good scorch resistance, calendaring, extrusion, coating, and other processing properties, as well as self-adhesive and mutual adhesion, and the surface should be smooth and bright after vulcanization or plasticization. The strength and abrasion performance of the covering rubber has a great influence on the service life of the conveyor belt. When the strength is 10-14MPa, the durability rate of the conveyor belt is 100, when the tensile strength is 18-20MPa the durability rate is 120, and when the tensile strength is 25MPa or more the durability rate is 140.
- The core rubber material is in direct contact with the belt carcass, and it has the effect of bonding, isolating, cushioning, and enhancing the rigidity in the conveyor belt. The comprehensive performance should meet the following requirements: (1) It has good adhesion to the carcass and is easy to penetrate the fabric or between the strands of the steel cord to act as a “nail effect”. It also needs to be chemically combined with the fabric or steel wire. (2) The adhesive strength of the rubber material will not decrease due to the long-term repeated bending of the conveyor belt, surface pressure, and external impact. (3) Heat resistance must ensure that the performance of the conveyor belt does not significantly decrease after multiple hot joints and hot repairs. (4) It has high tear strength and rigidity, can provide proper stiffness for the conveyor belt, and has a certain degree of cushioning and resistance to the impact and puncture of foreign objects. (5) When the covering rubber is required to have the characteristics of flame retardancy, oil resistance, or heat resistance, the core rubber should also have the same performance. (6) It has a better ability to adapt to scorch processing.
Design of conveyor belt
The design scheme of the conveyor belt is determined by the equipment situation and the performance, form, and environmental conditions of the materials to be conveyed. Good design can not only ensure the use performance of the conveyor belt, extend the service life, but also reduce the manufacturing cost. Before designing, you should first understand the type, quality, and form of the material being conveyed, as well as the loading drop, conveying volume, flow-form, and conveying route and distance as the basic reference point of the design. The design content roughly includes structure, strength and safety factor, belt width and configuration, covering rubber, and cross reinforcement.
- The fabric core conveyor belt can be divided into single-layer, double-layer, or three-layer sandwich-type, multi-layer type, and integral core type depending on the structure of the fabric. The skim rubber thickness of the sandwich conveyor belt is about 1.5mm. The sandwich can improve the cushioning performance of the conveyor belt and adjust the cross rigidity; the multi-layer belt has many disadvantages due to its structure, and it has been limited to less than 4 layers. ; Compared with the multi-layer belt, the tension and elongation of the whole core belt when it enters the belt roller in use are more easily balanced, and it can withstand huge instantaneous impacts, and the mechanical joint strength is also high.
- Steel cord conveyor belts have different structures such as the longitudinal parallel arrangement of steel wires and the braiding of steel wires.
- The strength of the conveyor belt is mainly provided by the belt carcass. The safety factor is the ratio of the tensile strength of the conveyor belt to the maximum working tension. The factors related to the determination of the safety factor are the condition of the conveying material; the condition of the conveying equipment, such as the size of the driving roller wrap angle, starting conditions, management status, and operating cycle; the characteristics of the conveyor belt, such as the carcass material, the structure of the conveyor belt and the joint method Etc. The safety factor of the general fabric conveyor belt is 10~20, the high-strength belt is 10~14, the heat-resistant belt is 15~20, and the steel cord belt is 5.5~10. When choosing the safety factor, you should be cautious. Excessive emphasis on safety will increase costs. On the contrary, excessive emphasis on the economy will lead to the risk of shortening the life of the conveyor belt.
- The maximum size of the material is an important parameter that determines the belt width, followed by the conveying capacity. The conveyor belt is too narrow to keep the material stable on the conveyor belt. Configuration refers to the shape and structure of the conveyor belt, such as ribs, baffles, guides, grooves, tubes, fans, etc. Nowadays, the development of tube-shaped conveyor belts is rapid because it meets many comprehensive performance requirements such as environmental protection and up and down bending. Similarly, their width must be based on the size of the material, and then the inclination angle and conveying capacity can be considered.
- The design of the cover rubber is first to determine the type and quality of the rubber, followed by the thickness, and then the surface. The quality and thickness of the covering rubber are consistent with the service life of the conveyor belt. Olefin rubber has high resistance to impact wear and chemical corrosion, and has a large friction factor; PVC is not as elastic as rubber, but PVC is flame-retardant, oil-resistant, and has a better discharge and cleaning performance; The strength, flame-retardant, oil-resistant, and friction factor of CR AND NBR are higher than those of PVC.
- The surface shape of the cover rubber has a certain influence on the angle of delivery. A smooth flat belt can transport free-flowing material at an inclination angle of 18 degrees, while a PVC belt is limited to 12 degrees. Sometimes to increase the conveying inclination and save land and engineering costs, the covering rubber surface can be designed with various patterns, such as rough top cover, U-shaped chevron cover, V-shaped, eight-shape, etc.. to adjust the cover friction and increase resistance,improve the ability to grasp materials. Generally, shallow patterns with a pattern height below 10mm can increase the conveying inclination to 22~23 degrees. When the pattern height is 10~35mm, the inclination can be increased to 35~40 degrees.
- Cross reinforcement can improve the mechanical performance of the conveyor belt, and overcome the problem of the decrease of the impact resistance of the fabric conveyor belt after replacing the cotton canvas with synthetic fibers. For synthetic fiber fabrics, due to weaving technology and cost factors, the weft strength of the fabric decreases as the warp strength increases. Taking EP fabric as an example, the strength ratio of the warp to the weft of EP100 is 10:5, while that of EP630 is about 10:2. Although the warp strength of the steel cord conveyor belt is high, there is no tensile strength in the weft direction. To meet the special mechanical performance requirements of certain conveyor belts, such as cross rigidity, high impact resistance, tear resistance, cushioning capacity, and joint strength, the conveyor belt needs to be strengthened laterally. In addition to light conveyor belts that can use horizontal monofilament structure fabrics, the reinforcement method is generally to lay horizontal cords, rigid or flexible twisted fabrics, thin steel wire, steel bars, or synthetic fiber threads in the cover rubber of the conveyor belt (one or both sides), etc. This can increase the strength by 90 ~ 175kN/mm or higher. Steel cord belts are reinforced with synthetic fiber ropes, and the pull-out strength of the steel cord can be appropriately improved.
Rubber conveyor belt manufacturing process
The basic manufacturing process of rubber conveyor belts includes rubber compounding and processing, calendaring, extrusion, molding, vulcanization, and inspection/packing.
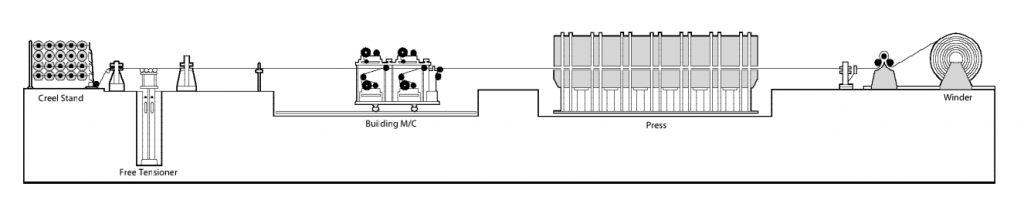
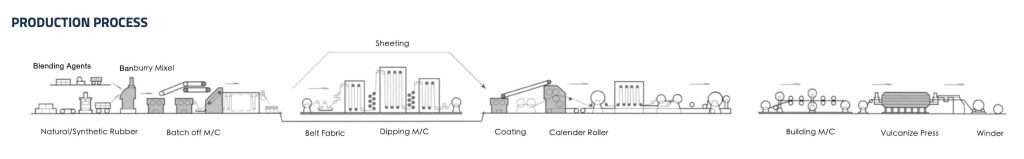
- The mixed rubber needs to be preheated before entering the calendar to reach a certain temperature and uniform plasticity so that it can evenly and smoothly pass through the gap between the rollers of the calendar. In the past, preheating was mainly based on the use of an open mill. Nowadays, cold feed extruders are mostly used.
- The calendering process mainly completes the fabric skimming, cover sheeting, and bonding of the belt blank and the covering sheet. Cotton and cotton blended fabrics need to be rubbed on both sides, and the fabric needs to be dried before rubbing to prevent blistering and delamination during vulcanization. The rubbing compound should penetrate the fabric structure to create a mechanical bond. It is very important to control the temperature when rubbing the glue and the temperature of the roller. Skimming is to stick a thin film on the fabric. Both synthetic fiber fabrics and steel wire rope woven fabrics are skimmed, usually on two sides, but the cotton fabric that has been rubbed can be skimmed on one side. Cover rubber calendering sheet is to make the compound rubber into a film with a certain width, thickness, and surface quality. The belt blank and the cover sheet are bonded by using a calendar to apply the cover rubber on both sides of the belt blank at a time. Some problems should be paid attention to in the calendering process:
(1) Process performance of rubber compound. The scorch performance, stickiness, and plasticity of the rubber compound will affect the preheating and calendering of the rubber compound. The temperature control and the rubber throughput need to be balanced, and the preheating capacity and the calendering ability need to be matched. Too high temperature or too much rubber will cause the rubber to accumulate and cause scorching. On the contrary, insufficient skimming will happen.
(2) Roller temperature Accurate temperature control is the basic condition for the normal operation of heat smelters, extruders, and calenders. The control program provided on the calendar should ensure that the equipment maintains the best temperature during operation.
(3) Tention The purpose of controlling the pretensioning force of the fabric is to ensure the strength of the finished conveyor belt and also to prevent the fabric from being damaged due to slack when the fabric passes through the gap between the rollers. The pre-tensioning force of the fabric is about 2% to 3% of its breaking strength.
(4) Thickness control is important for preventing waste and excessive rubber consumption. Automatic control must be reliable. If it is unreliable, it will be very dangerous.
- Forming is the process of neatly adhering multiple layers of the belt together longitudinally, sticking edge rubber on both sides, and covering rubber on the top and bottom to make a belt blank. The most basic requirement of forming quality is to put together the laminating at one time while maintaining the same tension of each fabric layer. Most of the forming of the conveyor belt in China is carried out on the workbench with a cloth guide frame, laminating roller, and take-up guide device, which is free bonding under tension-free control. In this way, the tightness of the fabric layers of the belt blanks obtained is not uniform, which affects the strength and load capacity of the conveyor belt. It is prone to vivid edges, deviation, and running length during use.
- In addition to the pursuit of the best physical properties and dimensional accuracy in the full width, full-thickness, and full length of the conveyor belt, vulcanization should also pay attention to the straightness and appearance of the conveyor belt. Ensuring uniform tension is the key to giving full play to the performance of the conveyor belt. When determining the vulcanization conditions of the conveyor belt, it is necessary to consider: (1) The vulcanization rate of the core rubber and the cover rubber: the vulcanization rate of the core rubber is generally higher than that of the cover rubber (2) The thickness of the belt: the thickness increases and the vulcanization time correspondingly extend (3) the relationship between time and temperature: thicker conveyor belts and higher vulcanization temperatures are likely to increase the difference in the degree of vulcanization between the surface and the inside of the conveyor belt.
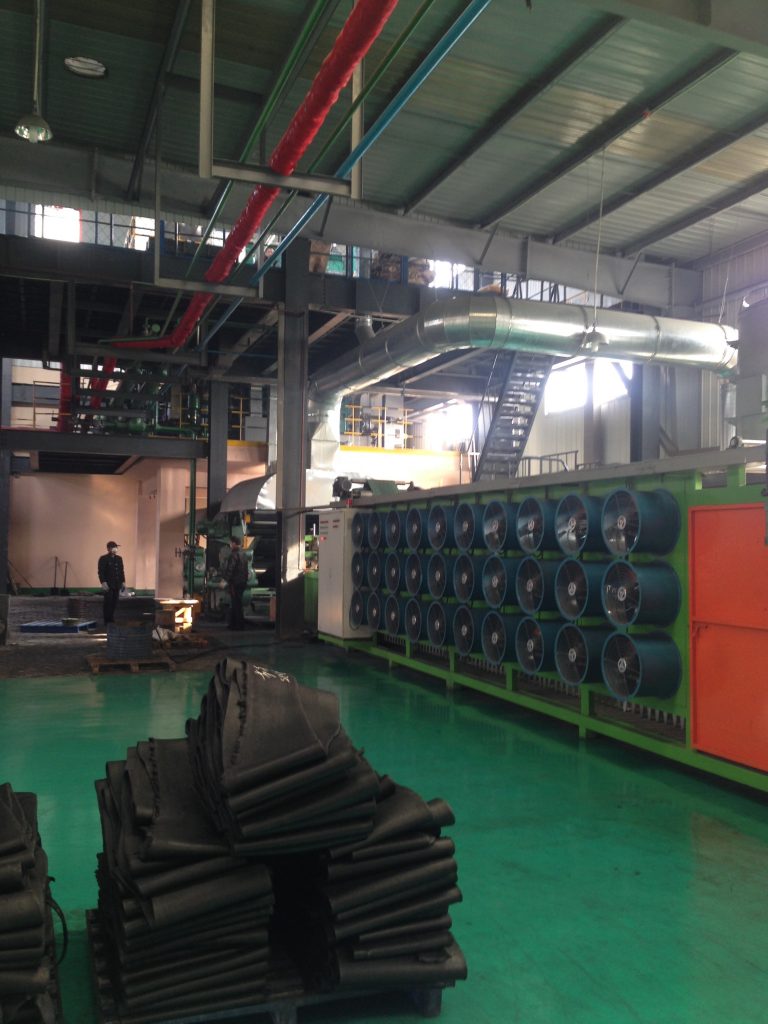
- Conveyor belt vulcanizing equipment mainly includes press vulcanizing machine, rotocure vulcanizing machine, and press continuous vulcanizing machine. The press vulcanizer has a long history of use, with a width of 2 to 3 m, a length of 10 to 15 m, and a pressure of 2.5 to 3.0 MPa, which has strong applicability. It is matched with guiding, reeling, clamping, and stretching devices. At present, the vulcanization of steel cord conveyor belts and deeply patterned conveyor belts must also rely on press vulcanizers. To improve productivity, the narrower conveyor belt can be vulcanized in two rows, or increase the number of hot decks, and vulcanize two or three at a time. The vulcanizing machine is economical and easy to manage.
- Rotocure vulcanizers have appeared in the 1930s, making the vulcanization process of the conveyor belt continuous, which is convenient to connect with the molding process and avoid the phenomenon of repeated vulcanization. Drum vulcanizing machine vulcanizing products are of good quality and low elongation, and the investment and floor space are both smaller than press vulcanizing machines. For ordinary fabric core conveyor belts and shallow pattern conveyor belts with a thickness below 15mm, drum vulcanizers are mostly used.
- Steel cord conveyor belts are commonly used for long-distance, high-speed, and large-volume bulk material transportation. The strength balance and straightness requirements of the steel cord conveyor belt are relatively high. Steel cord laid side by side in the belts must be flat, straight, and equidistant. The production process requirements are very strict. The steel cord conveyor belt production line generally includes cord pre-stretching device, combing-clamping, and tensioning device, belt forming cold press car, plate vulcanizing machine, traction clamping device, and reeling device, etc., with a total length of more than 100 meters. The core rubber and cover rubber are pre-laminated and put on the line. The cord traction, combing, and tensioning are completed on the production line, the core rubber and cover rubber are bonded, and the whole process of trimming, vulcanization, inspection, coiling, and cutting is completed. The tension should always be kept constant throughout the whole process. The deformation of the hot plate should be small, and the deformation of the hot plate should not cause the partial under pressure to produce scars. The production process needs to be managed by a program and monitored by a monitoring chain device to ensure the quality of each vulcanization.
How to join rubber conveyor belt
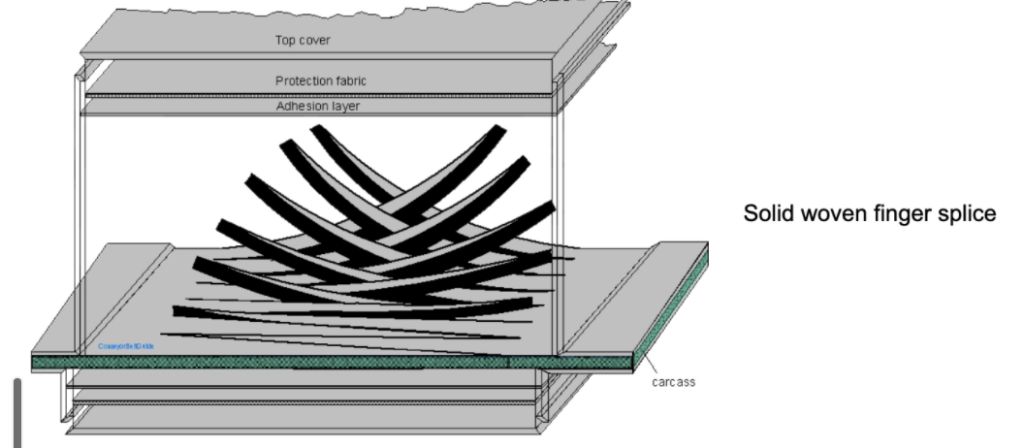
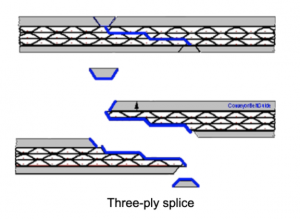
- Conveyor belts are rarely processed into endless under working conditions at one time, and most of them are made into large-length open-ended belts in continuous production, and then transported to the worksite in rolls. The belt needs to be connected into an endless belt according to the conveyor machines. Even though it is a light-duty conveyor belt, which is also produced in the factory into large-width and long-length tapes, which are then cut and connected into endless belts of the required length. Therefore, the connect ability of the conveyor belt is one of its necessary characteristics. The connection process of the conveyor belt must maintain the maximum strength and flexibility of the belt as much as possible. It also needs to be easy to operate and can be installed and used as soon as possible. So the strength of the joint is undoubtedly the weakest part of the entire belt.
- The splicing methods of the fabric core conveyor belt are a mechanical method, hot vulcanizing method, and cold bonding method, among which the hot vulcanizing method is the most reliable.
- The mechanical joint method is the traditional way of splicing conveyor belts. Although the strength loss of the joint using this method is relatively large, and the service life is short, its operation is simple, the joint is fast, and the running problem can be dealt with on time, so it is still in use today. The PVC/PVG belt has strong adaptability to the mechanical splicing method with its special braided structure.
- The hot vulcanizing method is a joint method in which the conveyor belt carcass is peeled off along the length direction, and then the carcass at both ends are lapped and bonded with an adhesive material, and then heated, pressurized and vulcanized (cured). This method has high strength, stable and reliable joints. The main technical parameters that affect the strength of the joint are the cut strength of the bonding part, the lap length, and the number of steps. The lap length is proportional to the breaking strength of the carcass, the higher the strength of the fabric, the longer the lap length needs to be properly extended. Since the fabric strength of the conveyor belt has been standardized, the overlap length of the joint is also standardized.
- The use of neoprene adhesive to cold bond the rubber belt brings great convenience to the on-site construction. Although the joint strength and operating temperature are limited, and the service life and reliability are not as good as thermal bonding, it is still welcomed by users and is used more and more widely. To improve the reliability of the joint, special attention must be paid to the quality of the adhesive, and a curing agent and surface treatment agent must be used in conjunction with it. The cold glue bonding operation procedure is basically the same as the thermal bonding method, except that the heating process is omitted. The joint form should adopt an oblique cut joint, and the cut-out filling strip should be concave and not protruding. In this way, when the conveyor belt passes through the roller and the cleaner, the joint angle enters first, the joint is less likely to be scrapped, and the operation is safer.
- The splicing of steel cord conveyor belts can only be achieved by hot vulcanization. It does not connect the steel wires one by one but obtains the joint strength through the adhesive strength of the rubber between the steel wires and the steel wires. The steel cord is wrapped in rubber, and the adhesive force between the rubber and the cord increases with the increase of the bonding length, and even exceeds the breaking strength of the steel cord. This is the theoretical basis of the steel cord belt joint. The design of steel cord belt joints in various countries in the world is carried out in accordance with DIN 22131 standard.
- The technology of joint manufacturing is very important. The main points are: (1) Keep less dust and moisture pollution at the operation site; (2) Operators need to be trained and understand the consequences of shoddy work; (3) Complete tools and equipment. The prepared rubber should be consistent with the performance of the belt, without any pollution or scorching, and the specifications are suitable for the requirements of the joint; (4) The transition layer at the connection part must have a certain slope; (5) The thickness of the rubber film remaining on the wire rope after cutting and polishing should be as consistent as possible; (6) Avoid scorching due to grinding and do not use solvents to clean and brush too much rubber glue. (7) The arrangement of joints must meet the design requirements, and the steel wire ropes should be laid straight, and the conveyor belt should be straightened by the central steel wire rope; (8) The core rubber filled between the ropes must be wide enough and combined with the upper and lower covering rubber; (9) When vulcanizing after splicing, side irons must be fixed on both sides to ensure that the bandwidth and thickness of the joint part are consistent with other parts; (10) The vulcanization pressure is 0.8 to 1.0 MPa, the temperature is 140 to 150 ℃, and the vulcanization time can be roughly calculated as 3 minutes per millimeter of belt thickness. The more accurate vulcanization time can be comprehensively determined according to the vulcanization conditions of the rubber compound and the belt thickness. After vulcanization, the belt should be completely cooled down before opening the hot plate.
Conveyor belt performance
- Strength is the most basic performance parameter of the conveyor belt, and it is the basic parameter that reflects the conveyor belt’s tensile strength, transmission power, and ability to support the conveying materials. The strength of the conveyor belt depends on the type and strength of the carcass material used. It can be calculated approximately based on the total strength of the fabric layer or the sum of the strength of a single steel cord. Because the breaking strength of the conveyor belt is non-uniform along with the thickness and width of the belt, and various parts of the conveyor belt are affected by different external effects and joints during use, the actual strength of the conveyor belt is much lower than the calculated value. Therefore the safety factor must be considered when calculating the strength of the design.
- The elongation characteristics of the conveyor belt have an important impact on the performance of the conveyor belt. The elongation of the fabric core conveyor belt includes three aspects: (1) Initial elongation: When the conveyor belt is installed, a certain stretching tension is applied to produce the initial elongation, and its function is to eliminate the phenomenon of slack. (2) Elastic elongation: when the conveying belt is running, it is produced from the tight side to the loose side. The elastic elongation is continuously produced and restored in each cycle of the belt, and it is the main part of the conveying belt elongation. (3) Permanent elongation: The part of elastic elongation caused by continuous bending and deformation that is stable and no longer recovers is called eternal elongation. It is continuously growing and runs through the entire service life of the conveyor belt. An excessively large permanent extension is unfavorable to the operation of the conveyor belt, and efforts are required to reduce at the manufacturing side. The initial elongation of the steel cord conveyor belt is very small, and there is no increase in elongation during the tension cycle. The permanent elongation of polyester is smaller than that of nylon. Therefore, the core material should be selected according to different purposes.
- Longitudinal bending is the performance of the conveyor belt bending on the driving, rotating, and redirecting rollers. The outer layer of the conveyor belt running around the rollers is stretched while the inner layer is compressed. Excessive stretching of the outer layer will cause fatigue and loss of strength. The inner layer will wrinkle under compression, which also reduces the strength. Due to the rigidity of the belt, the actual roller wrap angle is slightly smaller than the calculated value (about 14-22 degrees), which affects the transmission of force, which is also the bending resistance. It is not difficult to imagine that the more layers of the conveyor belt, the thicker and harder the belt body, the worse the flexibility of the belt, the greater the bending resistance, the shorter the service life of the conveyor belt, and the higher the energy consumption. It is also one of the reasons why the multilayer belt needs to be reduced.
- The situation of the overall braided core conveyor belt is different. The warp threads of the conveyor belt are not arranged in a straight line in the fabric but walk obliquely through the weft threads. The stress generated can be balanced around the roller, and the conveyor belt is not damaged, so the longitudinal bending performance is better than a multi-layer belt. The steel cord of the steel cord conveyor belt is twisted and twisted into a rope. The stress is also consumed between the inside and outside of the steel cord. Therefore, it exhibits a certain degree of flexibility and is easier to pass through small-diameter rollers.
- Belts for conveying bulk materials, trough-ability is an effective measure to improve conveying capacity. At present, the maximum trough angle of the conveyor belt is 55 degrees. Trough-ability reflects the ability of the conveyor belt to bend laterally, that is cross-rigidity. The trough ability depends on the belt width, the quality of the carcass material, and the thickness of the belt. If the rigidity is too large and the groove formation is insufficient, the conveyor belt can only be supported by the edges during operation, resulting in excessive wear on the belt edges and rollers. If the rigidity is insufficient and the groove is excessively formed, the conveyor belt will be too consistent with the groove shape of the idler during operation, and the conveyor belt will bend and wear at the contact of the idler, leading to early damage. The ideal trough is that the conveyor belt falls on the middle idler when freeloading, and contacts the middle and both side idlers at the same time during operation.
- Impact and tear damage are important reasons for the early damage of the conveyor belt. Common impact damage is obvious cover rubber damage or belt penetration. Obstruction of penetrating objects may cause long longitudinal tears. This is the most dangerous. There are also hidden damages, there is no obvious damage to the covering rubber surface but the internal carcass is damaged, the strength is reduced, and a weak part is formed. With the extension of the operating time, it will continue to expand and there is a risk of causing the conveyor belt to break.
- The impact resistance of the conveyor belt is closely related to the thickness of the carcass material, interlayer core rubber, and cover rubber. The cotton canvas cloth has a thick layer and has good impact resistance. Because the energy absorption mainly occurs in the rubber layer, thicker interlayer rubber is beneficial to improve the impact resistance, but the deformation is limited by the fabric when subjected to impact, and the cushioning capacity is limited. Therefore, the thickness of the covering rubber should be increased for the fabric core conveyor belt and the steel cord conveyor belt that can withstand greater impact, and the transverse reinforcement layer structure should be adopted. For the fabric core conveyor belt, increasing the weft density and weft strength of the fabric can improve the impact and tear resistance of the conveyor belt, and it is conducive to the mechanical joint of the conveyor belt.
- The conveyor belt is driven by friction, the friction factor between the transmission surface of the conveyor belt and the drive roller is between 0.1 and 0.5. The size of the friction factor is related to the variety of elastomer materials and the wet state of the roller surface, as well as the changes in operating speed, pressure, and humidity. The friction performance of the working side of the conveyor belt has a great influence on the stability, loading, and unloading, and cleaning performance of the conveyed materials. Abrasion is the wear and tear of the cover rubber caused by the impact of the conveyed material on the conveyor belt. The main forms of wear are impacted cutting wear, deviation wear, friction wear, fatigue wear, and swelling wear. Among them, impact cutting wear and swelling wear (oil pollution swelling) are the most serious. Reducing wear can extend the service life of the conveyor belt. One of the effective measures to reduce wear is to select high wear-resistant strength cover rubber and increase its thickness. The second is to improve the operating conditions, including reducing the size of the material, the drop of the feeding point, and preventing the material from jumping and slipping on the conveyor belt, so that the feeding direction and speed are consistent with the operation of the conveyor belt. It is also necessary to strengthen maintenance to prevent deviation and pay attention to oil pollution.
Conveyor Belt Test
- The following routine tests should be carried out on the conveyor belt: tensile strength and elongation, abrasion, 10% constant load elongation, trough-ability, straightness, and adhesion strength. Size deviation: belt length, belt width, belt thickness, upper and lower covering rubber thickness, steel cord position in the belt.
- Characteristic test of flame retardant conveyor belt: static conductivity, the fire test, drum friction test, propane combustion in the channel.
- Dynamic test: The dynamic fatigue life of the fabric belt joint; the permanent elongation and elastic elongation of the fabric belt under dynamic load; the dynamic fatigue life of the steel cord belt joint; The dynamic fatigue pull-out strength of the steel cord;


















Thanks for sharing the working principle of the rubber conveyor belt, which includes types, formulas, design, and its manufacturing process. For the last many days, I was looking for this same information and now I have found the relevant one. Great job.